Binary Search in C Programming

A binary search algorithm is used to find the position of a specific element in a sorted array. Instead of checking each element one by one (like linear search), binary search is based on divide and conquer technique which means it will divide the array in two halves, and the search continues in the half where the target element could exist until the element is found or the search space becomes empty.
What Is a Sorted Array?
A sorted array is one where elements are arranged in ascending or descending order. Binary Search only works on sorted arrays, so make sure your array is sorted first.
How Binary Search Works
Binary Search uses three main variables:
- low → starting index
- high → ending index
- mid → middle index
Algorithm Rules:
- If
a[mid] < key, search the right half (low = mid + 1). - If
a[mid] > key, search the left half (high = mid - 1). - If
a[mid] == key, element is found.
Let’s consider the following array and we want We want to check whether 70 is present in the array. We store the value to search in a variable, e.g., key = 70.

Initialize Pointers
Set two markers:
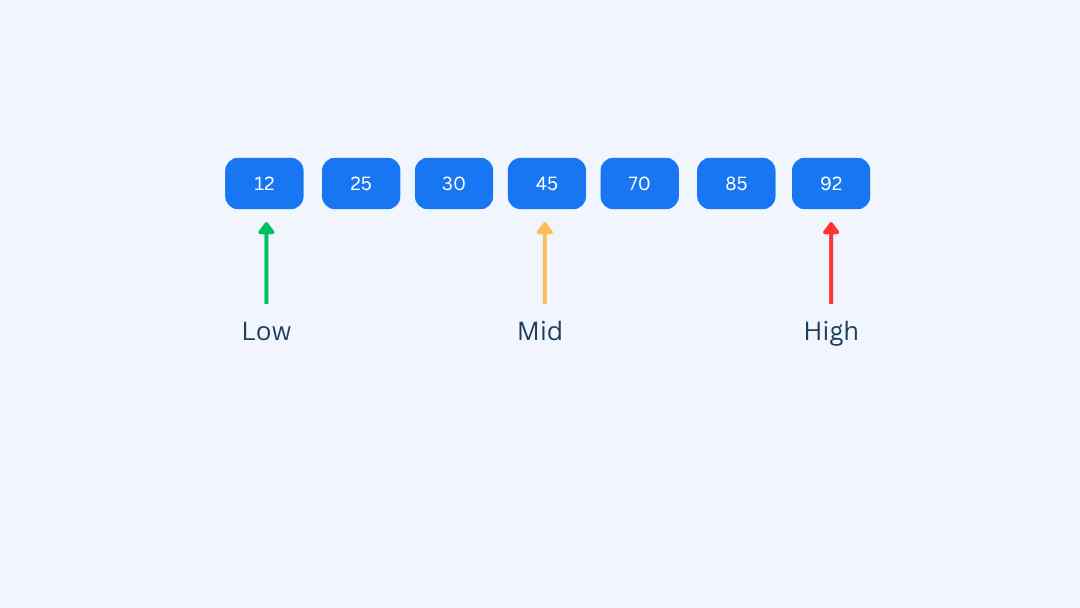
- low → start of the array (0, pointing to 12)
- high → end of the array (6, pointing to 92)
These pointers define the current search range.
Determine the Middle (Mid)
Compute the middle index of the current range:
mid = (low + high) / 2 = (0 + 6) / 2 = 3
arr[mid] = 45
Compare with Target
Now we compare the key with arr[mid]:
- If
key == arr[mid], the search is complete. - If
key > arr[mid], search the right portion by updatinglow = mid + 1. - If
key < arr[mid], search the left portion by updatinghigh = mid - 1.
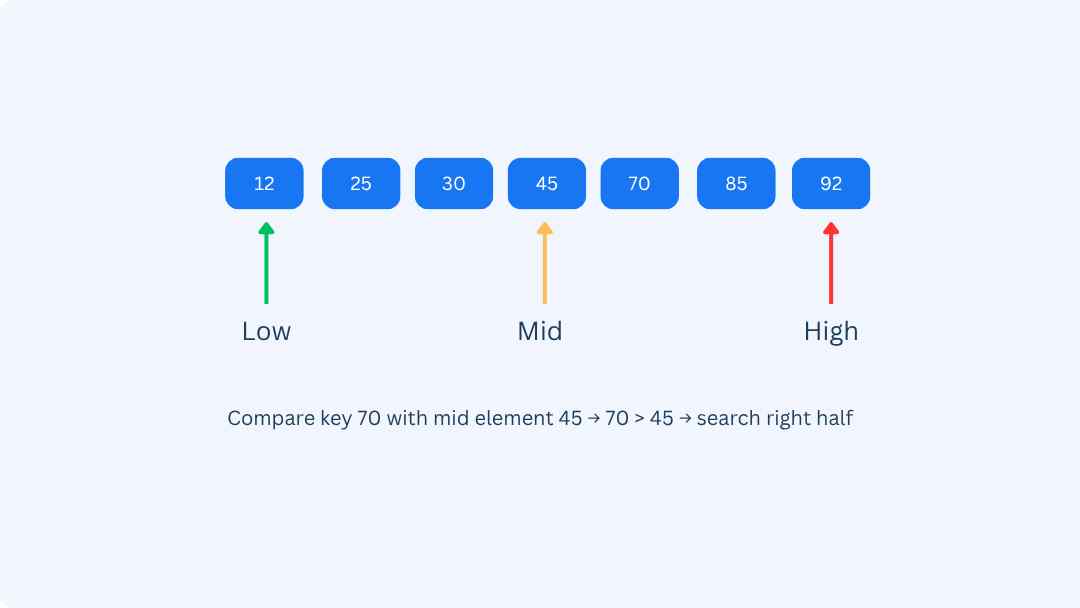
Step 1 Result: 70 > 45 → move to the right half
low = 4, high = 6
Next Middle
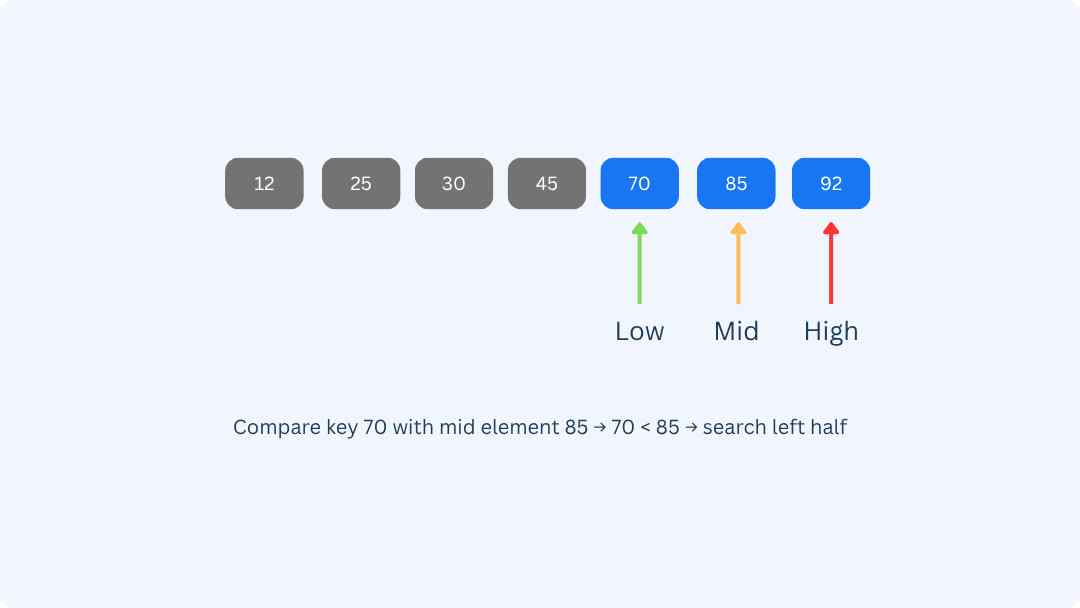
Calculate the new mid index in the updated range:
mid = (low + high) / 2 = (4 + 6) / 2 = 5
arr[mid] = 85
Compare: 70 < 85 → the target must be on the left side
high = mid - 1 = 4, low = 4
Final Step

Now the search space is reduced to a single element:
mid = (low + high)/2 = (4 + 4)/2 = 4
arr[mid] = 70
Since arr[mid] matches the key, we have found the target element!
Watch How Binary Search Works Step by Step
Curious how binary search finds an element so quickly? Try this animation to see the algorithm compare elements and adjust its search range in real time!
Binary Search Working Example
We will search for 70 in this sorted array:
Pesudo Code Of Binary Search
We are moving towards the Algorithm of Binary Search.
Algorithm of Binary Search
Binary Search Program in C
Advantage of Binary Search
Binary Search is simple and easy to implement, making it a good choice for many application.
It is well suited for searching of larger data sets that are stored in external memory such as hard drive or in the cloud
Binary Search is faster than linear search especially in case of larger arrays
Disadvantage of Binary Search
For Binary Search the array should be sorted.We must first sort it before performing the search
The interaction of Binary Search with memory heiarchy i,e. Caching is poor
It can be less efficient than other algorithm such as hash table for searching of larger dataset that do not fit in memory.
When to use Binary Search
When the data are stored in Contiguous memory
when the dataset is sorted
When the data does not have complex structure.
Conclusion
So far our Binary Search article comes to an end but before ending we just conclude what are the things that we have learned today.
To conclude, it can be said that
Binary Search Algorithm allow us to find element in a sorted list. As Binary Search cannot be performed in case of an unsorted array.
The Time Complexity for Average Case and Worst Case is O(logn).
In order to perform Binary Search Algorithm the array elements should be sorted.
Binary Search is useful for building complex algorithm in Computer Graphics and Machine Learning









